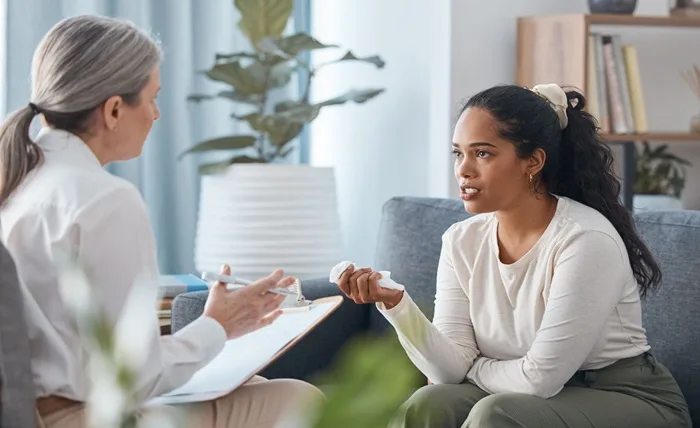
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) testing begins with a detailed assessment by a qualified mental health care professional. This assessment can include interviews, symptom tests, and a complete medical history evaluation to rule out other conditions. There is no singular ADHD testing method, and diagnosis often requires multiple evaluations. An exam by a primary care provider may also be conducted to check for health conditions that could cause similar symptoms to ADHD.
Getting an ADHD Diagnosis
Schedule an appointment with a licensed clinician to begin the ADHD testing process. Such clinicians include pediatricians, psychologists, and psychiatrists with expertise in diagnosing and treating ADHD. The diagnosis process involves a clinical interview, behavior rating scales, and gathering information from multiple sources, including people from school, work, and home. Pediatricians may be the first professionals to identify ADHD in children. They can conduct initial assessments and provide referrals to specialists like child psychologists or psychiatrists for further evaluation. These specialists have advanced training and experience in diagnosing and treating mental health conditions, including ADHD.
In adults, ADHD is often diagnosed by psychologists and psychiatrists. An ADHD diagnosis is determined by the number and severity of symptoms, their duration, and the degree to which they cause distress or interfere with daily activities. A thorough clinical history evaluation can provide evidence of the early onset of symptoms, helping these professionals make an accurate diagnosis. They may also use instruments like the Adult ADHD Self-Report Scale, an 18-item self-report questionnaire, to assess ADHD symptoms. Other conditions that coexist with ADHD, such as anxiety, depression, and substance use disorders, must also be evaluated. The goal is to accurately diagnose and develop an effective treatment plan tailored to each individual’s needs.
Understanding ADHD
ADHD is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects individuals of all ages, including children and adults. Persistent patterns of inattention and hyperactivity are common characteristics of this condition. If these symptoms are frequent and severe, they may affect an individual’s quality of life. ADHD is divided into three types, which include inattentive, hyperactive-impulsive, and combination.
Predominantly Inattentive Presentation
Individuals with predominantly inattentive ADHD presentation may struggle with attention and focus, and they may not exhibit the hyperactivity or impulsivity commonly associated with ADHD. Symptoms may include difficulty paying attention to details, trouble staying focused on tasks or activities, forgetfulness, and being easily distracted. Individuals with inattentive ADHD might also have problems with organization, following instructions, and completing tasks. Despite these challenges, individuals with inattentive presentation are usually less disruptive in social settings than those with hyperactive-impulsive presentation, which can lead to this form of ADHD being overlooked.
Predominantly Hyperactive-Impulsive Presentation
Predominantly hyperactive-impulsive presentation is characterized by symptoms of hyperactivity and impulsivity. Individuals with this form of ADHD may exhibit behaviors such as restlessness, excessive talking, and difficulty waiting in line. They may feel a need for constant movement and may frequently fidget or squirm. Individuals with this condition may have trouble focusing on quiet tasks such as reading. These individuals may also show signs of mood swings, anxiety, and lack of impulse control. Hyperactivity in adults can manifest as overworking, pressured speech, and stimulus-seeking behavior.
Combined Presentation
Symptoms of both inattention and hyperactivity-impulsivity characterize combined presentation ADHD. Combination ADHD symptoms may include difficulty focusing, forgetfulness, disorganization, restlessness, excessive talking, and impulsiveness. This combination can significantly interfere with daily functioning and development. Recognizing and understanding these symptoms is necessary for effective management and treatment.
With early diagnosis and appropriate interventions, individuals with combined presentation ADHD can manage their symptoms effectively and lead successful lives. Consider getting tested for ADHD if these symptoms are chronic and cause significant impairment in at least two of the following settings: home, school, work, or social. If you or your child’s symptoms persistently disrupt daily life and activities, it may be time to consider getting a comprehensive evaluation by a trained healthcare provider.
Schedule an Appointment for ADHD Testing
ADHD testing can provide you with a deeper understanding of yourself or your child. This enhanced awareness helps individuals better manage and treat their ADHD symptoms. Because ADHD can present in various ways, like inattentiveness and hyperactivity, a professional assessment and diagnosis can help individuals understand the root causes of behaviors affecting their lives. ADHD testing and diagnosis can help enhance daily productivity and minimize the impact of untreated ADHD symptoms. Contact your healthcare provider today to learn more about their ADHD testing services and schedule an appointment.